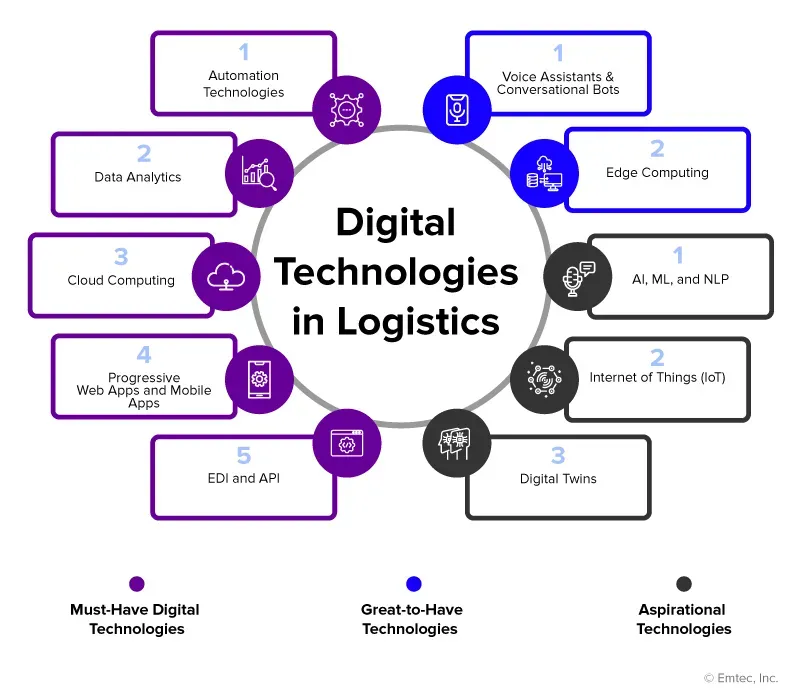
New technologies reshaping manufacturing and logistics are redefining how products are designed, produced, stored, and delivered, setting a new standard for organizational performance. From smart manufacturing floor sensors and interconnected equipment, organizations can gather real-time data that powers faster, more informed decisions and reduces waste. The rise of industrial IoT binds machines, tools, and systems into a cohesive network, enabling predictive maintenance, smoother operations, and near-zero unplanned downtime across facilities and the supply chain. These capabilities improve visibility, speed, and precision throughout the end-to-end value chain, empowering teams to optimize inventory, scheduling, and transportation with greater confidence. As adoption accelerates, leaders who align technology investments with measurable outcomes—such as higher throughput, enhanced resilience, and better customer experiences—will stay ahead in competitive markets.
Viewed through the lens of Industry 4.0, this transformation hinges on connected operations, intelligent automation, and real-time analytics that turn data into actionable insight across plants and warehouses. Organizations are building smart factories powered by digital twins, edge computing, and cloud platforms that expose end-to-end visibility and enable proactive planning. By focusing on scalable data governance, interoperability, and workforce upskilling, leaders can harvest the benefits of automated logistics, resilient supply chains, and accelerated product delivery without sacrificing security.
New technologies reshaping manufacturing and logistics: leveraging smart manufacturing and the industrial IoT to boost visibility and resilience
Across factories and distribution centers, the convergence of smart manufacturing and the industrial IoT creates a connected operating model. Sensors, edge devices, and cloud analytics generate real-time insights into equipment health, production throughput, and inventory movement. This visibility enables proactive maintenance, reduced downtime, and more accurate demand sensing, all of which strengthen resilience against disruptions.
With integrated data streams and standardized interfaces, teams from manufacturing, logistics, and IT can collaborate on optimization initiatives. Predictive maintenance, energy efficiency, and resource utilization improvements become continuous, supported by AI-driven analytics that translate data into actionable decisions. In logistics, IoT trackers and sensor data improve tracking accuracy and ensure product quality across the supply chain.
Digital twins, AI in manufacturing, and logistics automation: enabling end-to-end visibility and adaptive supply chains
Digital twins provide a living model of physical assets or end-to-end processes, enabling scenario testing before committing to real-world changes. By simulating line changes, layout adjustments, or inventory policies, organizations can optimize throughput and reduce risk. Digital twins also support remote monitoring and maintenance planning, aligning operations with demand signals powered by AI in manufacturing.
Together with logistics automation, digital twins and AI empower smarter routing, warehouse optimization, and labor planning. Autonomy in picking, sorting, and packing reduces errors and speeds up fulfillment, while real-time analytics from industrial IoT devices informs decision-makers about capacity, constraints, and supplier performance. The result is a synchronized, adaptive supply chain that can respond quickly to disruptions or shifts in customer demand.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do smart manufacturing and the industrial IoT contribute to the New technologies reshaping manufacturing and logistics?
Smart manufacturing and the industrial IoT form the technology backbone of modern factories and supply chains. Sensors, connected devices, and real-time data streams enable predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, and continuous process optimization on the shop floor, while IoT-enabled visibility in warehouses tracks inventory, location, and condition. The result is higher throughput, improved quality, and greater resilience backed by data-driven decision making.
In what ways do digital twins, logistics automation, and AI in manufacturing accelerate outcomes within the New technologies reshaping manufacturing and logistics?
Digital twins provide virtual representations of assets and processes to simulate changes, test scenarios, and forecast outcomes, speeding product development and operational optimization. When paired with AI in manufacturing, automation, and robotics—on the factory floor and in warehousing—these tools improve control, energy efficiency, and labor productivity. Logistics automation enhances end-to-end visibility and throughput through automated storage, autonomous systems, and real-time inventory management, enabling dynamic routing and responsive supply chains. Together, these technologies drive a more resilient, efficient, and scalable operation.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| The technology backbone: smart manufacturing and industrial IoT | Sensors, connected devices, and real-time data enable analytics and AI across the plant and supply chain; predict breakdowns, optimize maintenance, reduce downtime; in logistics, monitor inventory temperature, location, and condition for reliability. |
| Digital twins and simulation-driven decision making | Virtual models of assets or processes allow testing and forecasting without disruption; support proactive maintenance and agile responses; enable dynamic routing and warehousing optimization in logistics. |
| AI, automation, and robotics in manufacturing and warehousing | AI optimizes control parameters and energy use; predictive maintenance reduces downtime; cobots and autonomous robots perform repetitive or hazardous tasks; robotics speed up picking and packing and reduce errors in warehouses. |
| Cloud, edge computing, and cybersecurity considerations | Cloud and edge enable scalable storage and centralized analytics; edge reduces latency for time-sensitive tasks; cybersecurity is essential to protect data and operations; fosters IT–Operations–Supply Chain collaboration. |
| Logistics automation and supply chain visibility | Automated storage/retrieval, autonomous vehicles, and robotics improve warehouse movement; real-time visibility into inventory, transit, and supplier performance enables proactive decisions; end-to-end synchronization with manufacturing supports lean operations. |
| Implementation strategies and people considerations | Start with a digital strategy, pilot programs, and a prioritized roadmap; emphasize data governance and quality; prioritize change management and cross-functional collaboration across teams. |
| Real-world benefits and potential challenges | Benefits include higher productivity, shorter cycle times, improved quality, and more resilient supply chains; cost reductions come from efficiency and predictive maintenance; challenges include legacy systems, data interoperability, and cybersecurity; adopt a phased, measured rollout. |
| Case in point: a pathway to smarter operations | A phased transformation example: sensor upgrades for condition monitoring, pilots for predictive maintenance, automated storage pilots, and a digital twin to test queueing and throughput; scale across lines with analytics guiding energy, maintenance, and inventory strategies. |
| The path forward for organizations | Focus on a compelling business case, scalable data foundations, interoperability, and ecosystem fit; governance for data and cybersecurity; cultivate experimentation and resilience to realize the advantages of smart manufacturing, IoT, digital twins, and logistics automation. |
Summary
New technologies reshaping manufacturing and logistics are transforming how products are designed, produced, stored, and delivered, enabling higher quality, faster lead times, and more resilient supply chains. The integration of smart manufacturing and the industrial IoT provides real-time visibility and predictive insights across factories and warehouses. Digital twins allow safe testing and optimization of processes before implementation. AI, automation, and robotics raise productivity while improving safety. Cloud and edge computing support scalable analytics and near-instant decisions, with cybersecurity as a foundational requirement. Logistics automation links manufacturing and distribution for end-to-end synchronization, improving accuracy and customer satisfaction. Implementing these changes successfully requires clear strategy, robust data governance, workforce training, and a culture that embraces collaboration across IT, operations, and supply chain.